Key Takeaways
- GitHub Copilot has increased code volume and pull request frequency, which has shifted bottlenecks from coding to CI/CD and code review.
- The right-shift bottleneck shows up as more CI failures, more review cycles, and costly context switching that slows delivery and frustrates developers.
- Traditional CI/CD and review processes were built for human-paced workflows, so they struggle to keep up with AI-accelerated development at scale.
- Autonomous agents that fix CI issues and implement review feedback in real time help teams maintain flow, reduce rework, and control engineering costs.
- Install Gitar to offload CI failures and review rework so engineers can stay focused on product work.
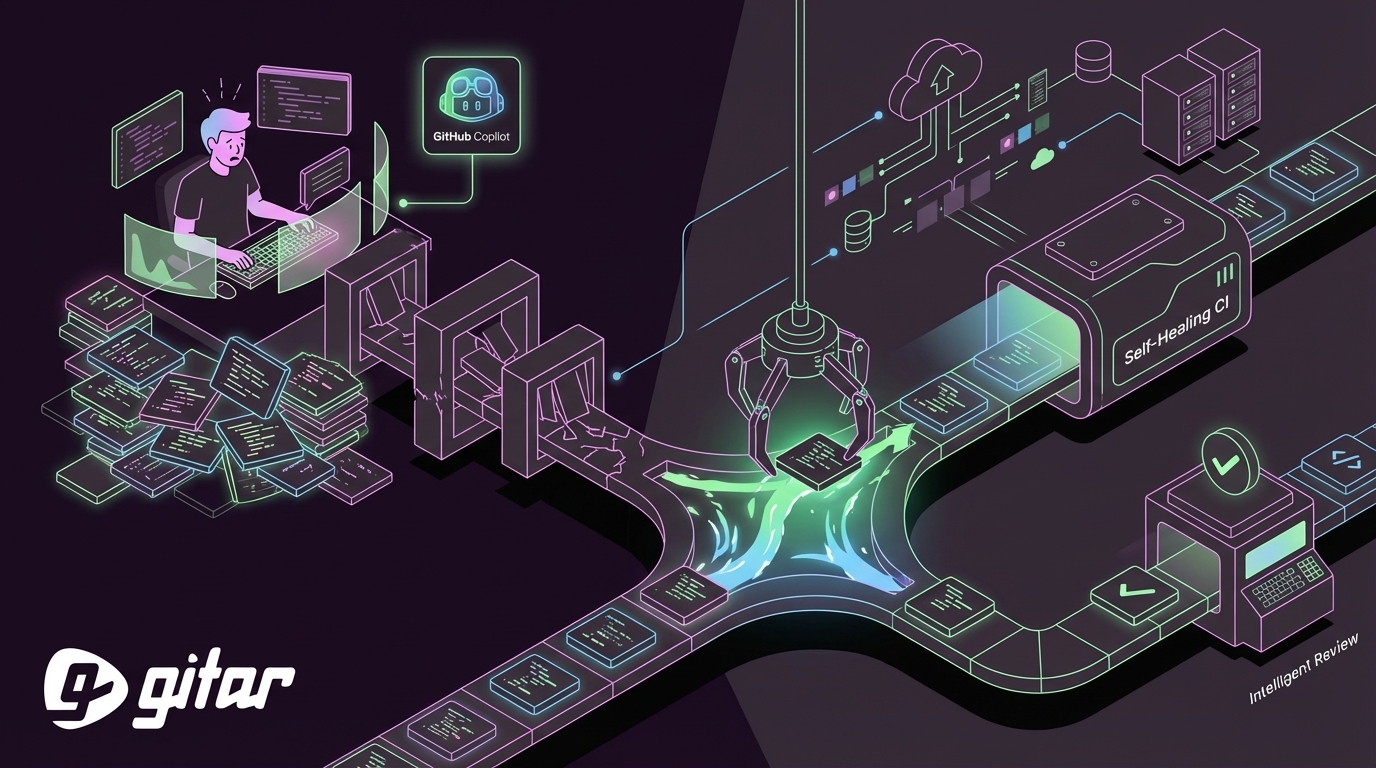
The AI Productivity Paradox: GitHub Copilot and the Right-Shift Bottleneck
GitHub Copilot’s Impact on Code Generation Volume
By early 2025, over 15 million developers were using GitHub Copilot, a 400% increase in just 12 months. Copilot now writes about 46% of the average user’s code, with rates as high as 61% in Java projects. Developers have been able to code around 51% faster on average, and average time to open a pull request in many enterprises dropped from 9.6 days to 2.4 days.
Understanding the Right-Shift Bottleneck
This faster code generation shifts the bottleneck to later stages of the pipeline. Post-commit processes such as CI/CD workflows, automated tests, and code review now absorb the pressure. More frequent follow-up edits after initial commits create extra CI runs and review cycles. Code can move faster than the systems that validate and integrate it.
Consequences for Engineering Teams
An 8.69% increase in pull requests per developer means more code to review, test, and fix when CI fails. Each failure pulls developers back into old branches and test logs. Context switching multiplies when teams work across time zones, and simple fixes can stretch across several days of asynchronous back-and-forth.
Modernizing Post-Commit Workflows for Engineering Team Efficiency
Limits of Traditional CI/CD and Code Review
Conventional CI/CD systems assumed a steady stream of human-paced commits. In a Copilot world, pipelines receive more changes, more often. Manual investigation of CI failures can consume a large share of developer time, and review comments that require several change rounds extend lead time even further.
Why Self-Healing CI and Intelligent Review Matter
Teams now benefit from systems that close the loop without constant human intervention. Self-healing CI means pipelines that can diagnose and fix common failures, then rerun checks until the pull request is green. Intelligent review actioning means tools that not only point out issues but also apply reviewer feedback and verify the result in CI.
The Cost of Inefficiency
A 20-developer team that spends just one hour per person per day on CI failures and review churn loses roughly 5,000 hours per year. At typical loaded engineering rates, that represents close to $1M of potential value shifted from product work to reactive debugging and rework.
Industry Momentum Toward Autonomous Solutions
Market data shows growing interest in agentic and autonomous coding capabilities, and AI coding tools are now evaluated as core parts of DevOps and platform engineering strategies. Organizations increasingly look for systems that not only suggest changes but also execute and validate them.
Gitar: Autonomous AI for Self-Healing CI and Actionable Code Review
How Gitar Improves Engineering Team Efficiency
Gitar is an autonomous AI agent that fixes failing CI pipelines and implements code review feedback. The agent takes on the repetitive work of reading logs, updating code, and rerunning checks, so developers can stay focused on design and feature development.

Key Capabilities That Matter for Teams
- End-to-end autonomous fixes: Gitar applies code changes, runs your full CI workflow, and only reports success when checks pass. Typical issues include lint violations, failing tests, dependency and build errors, and misconfigured scripts.
- Full environment awareness: Gitar emulates real CI environments, including specific SDK versions, multi-platform dependencies, and security tools such as SonarQube and Snyk. Fixes are validated against the same conditions that production code must pass.
- Review feedback implementation: Human reviewers can leave pull request comments addressed to Gitar, and the agent updates the code and pushes commits that satisfy the feedback.

- Time zone friendly workflows: A reviewer in one region can request changes before signing off. Gitar updates the pull request while the original author is offline, so the code is often ready to merge at the next workday start.
- Configurable trust model: Teams can begin with suggestion-only behavior, where Gitar opens commits or suggestions that developers approve. Over time, teams can move to auto-commit modes with rollback options when confidence grows.

Install Gitar to automatically fix broken builds and reduce review-driven rework.
Evaluating Your Approach: Build vs. Buy and Readiness for Autonomous CI
Trade-offs of Building Your Own Agent
Teams that try to build autonomous CI agents in-house must solve hard platform problems. The system needs to coordinate many users and pipelines, process noisy asynchronous signals, and preserve state across wave-based execution where several stages run in parallel and still share context. These demands often exceed the capacity of feature-focused engineering teams.
Specialized platforms such as Gitar already handle concurrency, environment emulation, permissions, and rollback. Adopting such a platform lets teams capture efficiency gains quickly instead of investing months of effort into bespoke automation.
Assessing Organizational Readiness
Effective adoption depends on alignment across roles. Engineering leaders need clear success metrics, DevOps teams need confidence in reliability and observability, and developers need easy ways to understand and override automated changes. Practical rollouts often start with lower-risk services and involve security and compliance teams from the beginning. Continuous feedback between platform engineers and developers helps refine policies and trust levels.
Strategic Pitfalls for Experienced Engineering Teams
- Relying only on suggestion engines: Some tools flag issues but leave implementation and validation to developers. This still forces manual fixes and extra CI runs.
- Overlooking the right-shift bottleneck: AI-assisted code generation without matching investment in post-commit automation creates an overloaded CI/CD stage.
- Underestimating context switching: Metrics that track only debugging time ignore the cost of regaining flow after interruptions.
- Using rigid automation controls: Automation that lacks gradual trust modes can meet resistance from teams that want to review early changes before turning on auto-commit behavior.
- Treating AI tools as point solutions: End-to-end software engineering evaluations now include testing and quality management, so tools that do not integrate across the lifecycle miss important optimization opportunities.
Competitive Landscape: Healing Engines vs. Suggestion Engines
The market for post-commit automation falls into three broad categories.
|
Feature / Tool Category |
Gitar (Healing Engine) |
CodeRabbit (Suggestion Engine) |
“Big Model” Integrations (DIY Toolkit) |
|
Core Functionality |
Autonomous fixes, self-healing CI, review feedback implementation |
AI review suggestions and analysis |
General AI capabilities that require custom integration |
|
Actioning Fixes |
Applies changes, validates them, and targets green builds |
Suggests changes, requires manual implementation |
Requires custom engineering for actioning and validation |
|
CI Environment Context |
Full environment replication across platforms |
Primary focus at the git provider level |
Requires custom context and environment management |
|
Automation Scope |
Post-commit automation across CI/CD and code review |
Post-commit review assistance |
Broad potential scope with significant setup |
Healing engines such as Gitar automate the full path from failure detection to resolution. Suggestion engines keep engineers in the loop for final implementation. DIY big-model integrations offer flexibility but generally demand substantial platform investment to reach the same level of autonomy.
Install Gitar to add a healing engine on top of your existing CI and review tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does Gitar help manage the extra CI/CD workload that comes from GitHub Copilot adoption while maintaining engineering team efficiency?
A: Copilot speeds up coding and increases pull request volume, which in turn increases CI runs and failures. Gitar responds to failed checks by reading the logs, generating targeted fixes, and committing updates back to the pull request. The agent can rerun CI until the build passes, which creates a self-healing effect that keeps higher code throughput from turning into a bottleneck.
Q: How is Gitar different from AI code review tools like CodeRabbit for improving engineering team efficiency?
A: Code review tools such as CodeRabbit focus on identifying issues and offering suggestions. Gitar goes further by applying fixes, validating them against the full CI pipeline, and only presenting results when checks pass. This shift from suggestions to execution removes a large amount of manual work for developers.
Q: How does Gitar address security concerns when it writes and applies code changes?
A: Gitar uses a configurable trust model. Teams can begin in a conservative mode where all fixes are presented as suggestions that require explicit approval. As confidence grows, teams can enable more automated commit behavior, with rollbacks available when needed. Gitar also runs within the same CI environments that already include tools such as SonarQube and Snyk, so automated fixes still pass through existing security and compliance checks.
Conclusion: End-to-End Automation for 2026 Engineering Teams
AI-assisted coding has already changed how software is written, and by 2026 the constraint for many teams sits in CI/CD and code review. Without automation at these stages, the gains from tools like GitHub Copilot can be offset by more failures, more reviews, and more context switching.
Gitar helps close that gap by giving teams self-healing CI and actionable code review automation. Organizations that adopt this kind of autonomous post-commit layer can shorten lead times, reduce unplanned rework, and keep engineers focused on building product value.