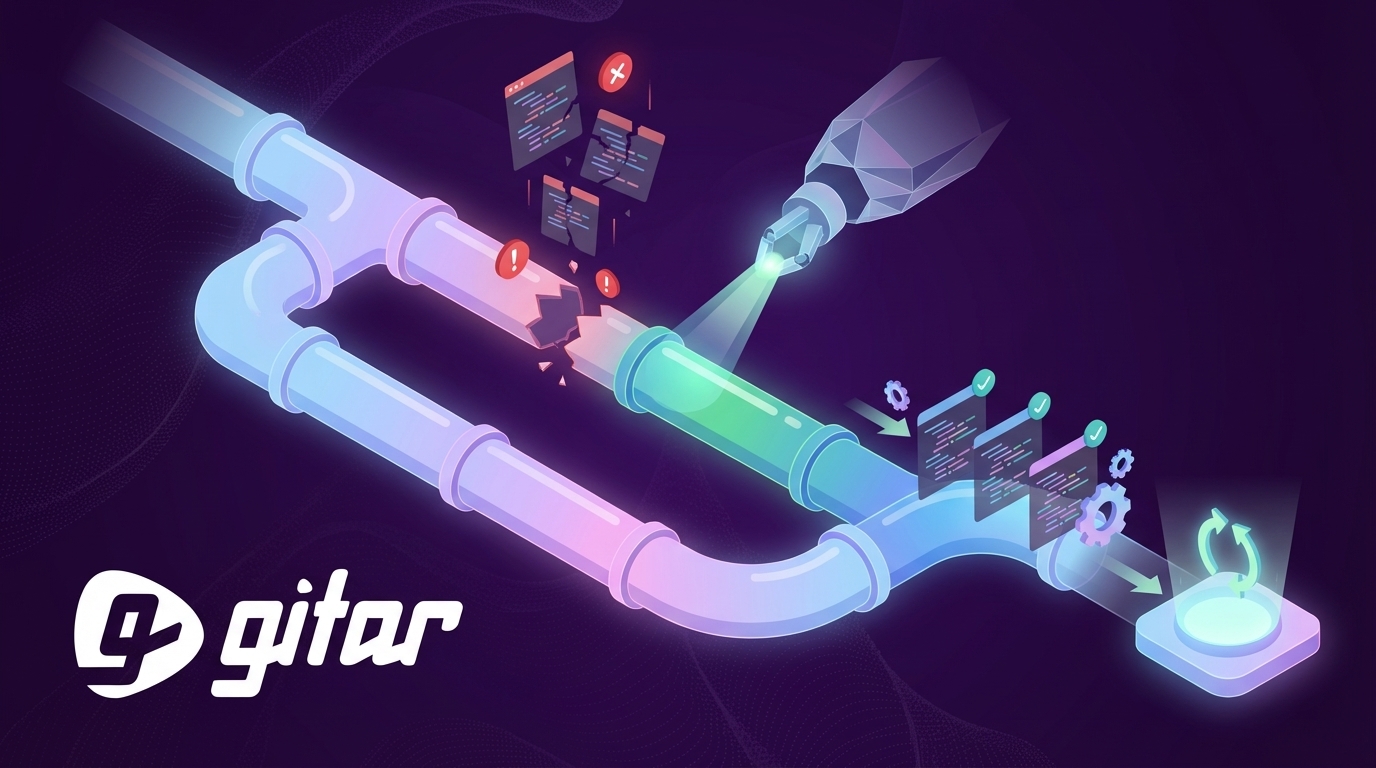
Key takeaways
- Autonomous self-healing CI reduces manual firefighting in pre-merge pipelines, where most failures and productivity losses occur.
- Healing engines close the loop from failure detection to validated fix, while suggestion engines stop at recommendations that still require developer effort.
- Engineering teams that adopt autonomous CI see clear ROI from reduced context switching, faster merges, and fewer blocked developers.
- Self-healing CI works best for frequent, well-defined failures and helps distributed teams reduce delays caused by time zones.
- Teams can use Gitar to automatically fix CI failures and resolve code review comments while keeping full control over automation.
The Imperative: Why Autonomous Self-Healing CI is a Strategic Necessity
Autonomous self-healing CI shifts CI/CD from reactive troubleshooting to proactive resolution. Pre-merge CI/CD failures occur far more often than post-merge failures, so individual developers feel the most friction while preparing changes for merge.
This friction carries a clear financial impact. A 20-developer team that spends one hour a day on CI failures and code review issues loses roughly $1 million in annual productivity at a $200 hourly loaded cost. That estimate does not include the extra time lost to context switching when short fixes interrupt deep work.
Suggestion-based AI tools reduce some effort but keep developers in the loop for implementation and validation. Developers still apply recommendations, rerun pipelines, and iterate when fixes fail. Autonomous self-healing CI closes that gap by applying and validating fixes on behalf of the team, so developers can stay focused on feature work.
Install Gitar to automatically fix broken builds and reduce time spent on CI noise.
Understanding Autonomous Self-Healing CI: A Strategic Framework
Autonomous self-healing CI extends beyond monitoring and recommendations. Monitoring tools notify teams about failures, and suggestion engines propose fixes. Healing engines instead take responsibility for resolving issues and confirming that pipelines succeed.
This framework rests on three capabilities:
- Intelligent analysis that understands failure context instead of only parsing logs
- Autonomous resolution that generates, applies, and tests fixes
- Environmental awareness that respects real CI/CD workflows and dependencies
Environment differences across development, staging, and production often cause flaky tests and deployment failures, so accurate replication is essential. Healing engines aim to bridge the full journey from detection to validated resolution, which turns many CI failures into background events instead of daily blockers.
The Gitar Difference: Introducing the Autonomous Healing Engine
Gitar implements autonomous self-healing CI as an AI agent that fixes failing pipelines and resolves code review feedback. The system applies code changes, runs CI in the full environment, and surfaces results when builds succeed or need further input.
Different roles gain distinct benefits:
- Software engineers reduce context switches, avoid repetitive debugging, and merge faster.
- Engineering leaders see higher throughput from unblocked developers and clearer visibility into CI-related costs.
- DevOps and platform engineers gain more reliable pipelines and less manual work managing recurring failures.
Teams calibrate trust through configurable automation levels. Conservative mode posts fixes as suggestions that require one-click approval. As teams gain confidence, they can enable auto-commit with rollback options to increase automation while keeping control.

Book a Gitar demo to see how autonomous fixes work in your CI pipelines.
Beyond Suggestions: How Gitar Achieves True Autonomous Resolution
Action-oriented architecture
Gitar implements a full action-validation loop. When a pipeline fails, Gitar analyzes logs and context, proposes code edits, applies changes in a branch or commit, and re-runs the pipeline. The system supports common failure types such as lint errors, test failures, build issues, and dependency conflicts.
The engine also manages CI events over time. It tracks concurrent jobs, handles asynchronous events, and coordinates across multiple waves of CI runs. This stateful behavior suits complex enterprise environments where many jobs and tools interact.
Environment replication for accurate fixes
Enterprise CI setups often use specific SDK versions, multi-SDK builds, and third-party tools such as SonarQube and Snyk. Gitar replicates these workflows so fixes reflect the same conditions that exist in real pipelines.
This replication reduces the risk of a fix that works in isolation but fails in CI. Gitar aims to produce changes that pass checks under real-world constraints, which increases trust in automated resolution and decreases false positives.
Intelligent code review assistant
Gitar also participates in code review. Reviewers can leave comments that include instructions for Gitar, and the system applies those changes directly to the pull request.
A reviewer in one time zone can request a refactor or removal of a feature, and Gitar updates the code and explains the changes in comments. The original author then starts the day with ready-to-review commits instead of an open feedback loop, which shortens review cycles for distributed teams.
Trust-driven automation controls
Gitar uses a graduated trust model to align with different team cultures. Teams often begin with suggestion-only mode to review each fix, then move to automatic commits as observed accuracy improves.
This approach allows cautious teams to maintain oversight while still gaining value. Teams that prefer higher automation can configure more aggressive settings and still rely on rollback options for safety.
Strategic Considerations for Implementation
Assessing readiness for autonomous CI
Successful adoption starts with understanding current CI pain. Teams can review failure rates, time spent on CI and code review issues, and existing automation. Industry trends show growing use of automation and AI in CI/CD, so early adopters gain an advantage in delivery speed and developer experience.
Implementation often begins with low-risk, high-frequency issues such as linting errors or simple test fixes. Teams then expand to more complex failures once they see consistent results.
Common pitfalls to avoid
Several patterns reduce value from autonomous CI initiatives:
- Expecting suggestion tools to behave like healing engines
- Underestimating the effort required to replicate full CI environments
- Enabling aggressive automation before teams feel comfortable with automated changes
- Building custom AI integrations that demand ongoing maintenance instead of using a purpose-built solution
Matching automation levels to team preferences keeps adoption steady. Teams that favor careful review can stay in conservative modes, while teams that already embrace automation can move faster.
ROI calculation for engineering leaders
For a 20-developer team, one hour per day spent on CI and code review issues equals roughly 5,000 hours per year. At a $200 hourly loaded cost, that work represents about $1 million in productivity.
If autonomous CI eliminates even half of that time, the organization saves around $500,000 per year, in addition to benefits such as fewer interruptions, faster feature delivery, and better developer morale.

Competitive Landscape: Healing Engines vs. Suggestion Engines
The autonomous CI market divides into healing engines that resolve issues end to end and suggestion engines that only recommend fixes. Clarity on this distinction helps teams choose tools that match their goals.
Comparison table: Gitar vs. traditional approaches
|
Feature category |
Gitar (healing engine) |
Suggestion engines |
Manual work |
|
Issue resolution |
Applies fixes, re-runs CI, aims for green builds |
Provides ideas that still need implementation |
Manual diagnosis, coding, and commits |
|
Automation level |
Configurable from suggestions to auto-commit |
Primarily recommendations |
No automation |
|
Environment context |
Operates in full CI environment |
Often limited or partial context |
Depends on local setup and expertise |
|
Time saved |
Reduces context switching and rework |
Varies by team and workflow |
Highest time cost |
Gitar focuses on the post-commit phase, where it ensures code passes quality gates and CI checks. Coding assistants and traditional AI reviewers still play a role earlier in the lifecycle, but Gitar acts as the agent that closes the loop in CI.
Install Gitar to start reducing manual effort on CI failures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Autonomous Self-Healing CI
What is the main difference between a healing engine like Gitar and a suggestion engine?
Healing engines such as Gitar apply and validate fixes in the real CI environment, while suggestion engines provide advice that still requires manual changes and re-runs. Healing engines aim to take a failure from detection to a passing pipeline with minimal developer involvement.
How does Gitar handle complex CI setups and tools?
Gitar replicates enterprise environments, including specific SDK versions, multi-SDK builds, and tools like SonarQube, Snyk, and snapshot testing frameworks. This context allows Gitar to propose fixes that align with existing workflows and compliance requirements.
How does autonomous self-healing CI help distributed teams?
Distributed teams benefit when reviewers can request changes that Gitar implements while the original author is offline. Pull requests move forward during off-hours, so teams in different regions experience fewer idle periods waiting for feedback or fixes.
How does Gitar balance automation with developer control?
Gitar provides multiple modes, from suggestion-only to auto-commit. Teams can start with full review of each fix, then gradually increase automation as they gain trust. Rollback options remain available so teams can revert changes that do not meet expectations.
What kinds of CI failures does autonomous healing handle best?
Healing engines are especially effective for recurring issues such as linting violations, formatting errors, simple test failures, dependency conflicts, and configuration mistakes. These failures occur often and follow repeatable patterns, which makes them ideal candidates for automation.
Conclusion: Reclaim Developer Productivity and Accelerate Delivery with Gitar
Autonomous self-healing CI turns many pipeline failures into background events instead of daily emergencies. Key CI/CD components such as code repositories and build servers sit at high operational and security risk, so automated detection and resolution support both productivity and resilience.
Gitar gives teams a way to regain hours spent on broken builds and slow review cycles while maintaining control over how automation behaves. Organizations that adopt self-healing CI position their engineering teams to focus more time on product work and less on pipeline maintenance.
Request a Gitar demo to see autonomous self-healing CI in your environment.